low end tidal co2 during cpr
Weil MH Bisera J Trevino RP Rackow EC. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 High quality chest compressions are achieved when the ETCO2 value is at least 10-20 mmHg.
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2
Likewise the Return of Spontaneous.

. Therefore the ETCO 2 is low. End-tidal CO2 When cardiac output is 5 litres per minute as in the healthy sedentary adult. During cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR adequate chest compressions generate a cardiac output of 17 to 27 allowing CO 2 circulation for exhalation.
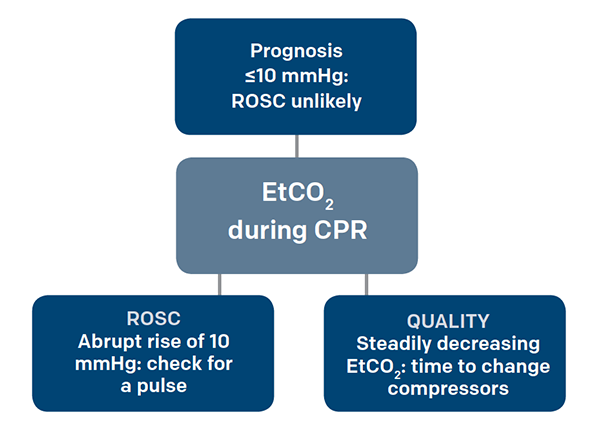
It has been suggested in several studies that a decline in ETCO2 is an indicative of the need to swap the personnel providing compressions during CPR. What should etco2 be during CPR. The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle.
Thus a detailed understanding of CO2 changes in various compartments is important in assessing and optimising the quality of an ongoing resuscitation. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing airway obstruction or respiratory distress. During CPR the blood flow to the lung may be so low that few alveoli are perfused.
Is inversely indicated by the amount of light that passes through the sensor. Therefore monitoring of ETCO2 provides very useful information to guide treatment during CPR 8-10. In the field monitoring ETco 2 during endotracheal-tube placement can verify correct tube placement and indicate tube dislodgement during transport.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. Crit Care Med 198513907-9. Cardiac output and end-tidal carbon dioxide.
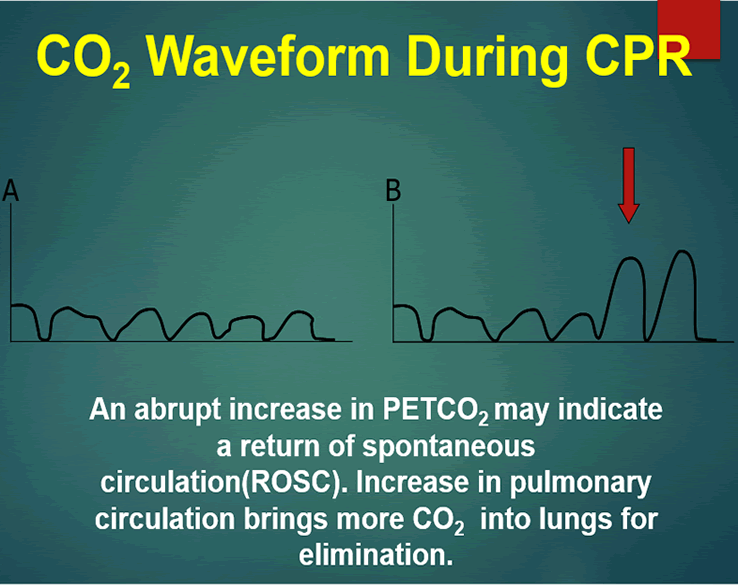
This is an example of capnography during CPR. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for confirming tracheal tube placement assessing the effectiveness of chest compressions predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC. End-tidal CO 2 monitoring during CPR is a relatively new area in which research is ongoing.
Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful Prognosis 20 mmHg at 20 minutes CPR - higher chance of ROSC almost no chance of. 35-45 mm Hg and ideal CPR will provide at least 14 of cardiac output. High CO2 levels are indicated by low infrared and low CO2 levels result in high amounts of light.
An end-tidal capnography waveform is a simple graphic measurement of how much CO 2 a person is exhaling. Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR. Measurement of a low ETCO2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient would indicate that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement.
End-tidal carbon dioxide. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. Low ETCO2 below 10 mm HG may be caused by either poor compression technique or from low perfusion and metabolism after a long downtime or shock despite good compressions.
Evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions is accomplished in the following manner. Evidence suggests a persistently low ETco 2 value and a widened Paco 2-to-ETco 2 gradient during CPR are associated with poor outcomes. It can also help the healthcare provider determine if the patient is being ventilated adequately.
Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are. Monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide during weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass in patients without significant lung disease. Since tidal volumes delivered with a bag-valve device are high many alveoli are ventilated but not perfused.
ETCO2 is a reliable indicator with. Current guidance recommends an end- tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 of 4045 kPa 300 338 mm Hg to achieve a low- normal arterial partial. Correlation of end-tidal CO2 to cerebral perfusion during CPR Partial correlation coefficients suggest that ETCO2 correlates with cerebral blood flow when changes in cerebral blood flow parallel changes in cardiac output.
Cardiac output and end-tidal carbon dioxide. Ornato JP Garnett AR Glauser FL. What should end tidal CO2 be during CPR.
What should end tidal CO2 be kPa. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. High quality chest compressions are achieved when the ETCO2 value is at least 10-20 mmHg.

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
Cpr Mobile Code Stand With Capnograph Capnography

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Emergency Intubations Capnography

Contribution Of Chest Compressions To End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels Generated During Out Of Hospital Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4

Potential Applications Of Capnography In The Prehospital Setting Journal Of Paramedic Practice
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram